A character LCD has been an interesting staff for novice micro-controller learner. Prior to the present of C programming for micro-controller, the student used the Assembly language to program this character LCD. It requires a few dozens of Assembly codes.
 |
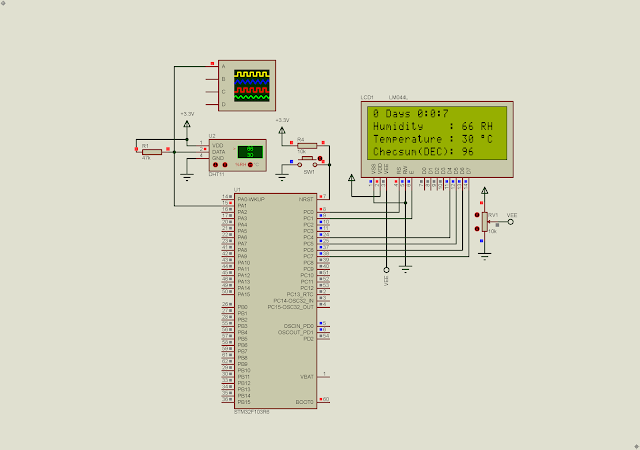
| Simulating Program In Proteus Using The STM32F103R6 |
Its original LCD controller was the Hitachi HD44780 chip. Currently it was replace by many other equivalent controller chip with low cost. For example, a 16x2 character LCD module costs around 1$.
 |
| A typical character LCD module |
.jpg) |
| A typical character LCD module |
 |
| Its Pins Diagram |
The interface between the micro-controller and this character LCD is a conventional parallel 8-bit data mode. However this LCD controller allow the program to use a 4-bit data transfer mode. You can see this tutorial for the LCD interface using 8-bit mode.
The LCD module is readable/writable. But we just write the command/data to this module is OK. The Register Select (RS) pin allow us to choose between command (RS=0) and data (RS=1). The Enable (E) pin allow the parallel data lath into the controller whenever there is a transition from High To Low.
I use the STM32CubeIDE to write this code. It's very easy to use and it's free of charge. We need to register first before it allows us to download this IDE.
I select a number of output pin in code configuration wizard before it can generate the core source codes.
 |
| STM32F103R6 Pin Configuration In STM32CubeIDE |
I need to write a few C functions to send the command and data to the LCD. And then I need to initialize the LCD module.
Click here to download its source file.
For other similar posts please check,
- Getting Started With STM32F103C8T6 Module with STM32CubeIDE
- STM32F103C8T6 Blue Pill SysTick and Multiplexing Display Example
- STM32F103C8T6 Blue Pill Switch And Multiplexing Display Interface Using SysTick
- STM32F103C8T6 Blue Pill SysTick LED Blinking
- STM32F103R6 Common Anode Seven Segments Display Example
- STM32F103R6 Common Anode Seven Segments Display And Switch Interfacing
- STM32F103R6 Simple 2-Digit Multiplexing Display And Switch Example
- STM32F103R6 SysTick And Digital Clock Example
- STM32F103R6 SysTick Two-Digit Multiplexing Display and Push Button
- LED Blinking With STM32F103R6 Using SysTick
- STM32F103R6 SPI Interfaces To SN74HC595N Shift Registers
- STM32F103R6 GPIO Interfaces To A Character LCD In 8-Bit Mode
- STM32F103R6 SPI Interfaces To A Single Seven-Segment Display



No comments:
Post a Comment